Fidel CastroAKA Fidel Alejandro Castro Rúz

Born: 13-Aug-1926
Birthplace: Mayari, Cuba

Gender: Male
Religion: Atheist
Race or Ethnicity: Hispanic
Sexual orientation: Straight
Occupation: Head of State![[image.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjQgLsP8ykRNT1VPdH0Xuf4WAnhFhbPiOR6KcxVXwSXOXYYa4gHBGWzytu2HfbkaM201SjUIWVMGHkMPpVZoRqG60Yx1KLieMvPA4P_JfxH1a3T3TlV2pA8XTnUyuMSX8yBthrmgygdHr_X/s1600/image.jpg)
Nationality: Cuba



On 26 July 1953, Fidel Castro led about 150 men in an attack on Moncada barracks, the strongest garrison of Fulgencio Batista. Batista was Cuba's dictator then, with friendly relations with the US government. Dozens of Castro's men were killed in battle, and Fidel was charged with treason. At his trial, he delivered an impassioned two-hour closing argument that was widely but clandestinely circulated under the title History will absolve me! It was a kangaroo trial, and Castro was sentenced to 15 years in prison, but a public groundswell called out for amnesty, and Castro was released in 1955. After a brief period of exile in Mexico, Castro's triumphant return came in 1959, when his next attempt at revolution succeeded. The brutal Batista government was overthrown, and replaced by the brutal Castro government.
History will absolve me was rewritten as a blueprint for Castro's communist regime, and American-owned businesses in Cuba were nationalized. Castro kept many of his promises -- Cubans have free health care, education, and a low level of homelessness, but the society has suffered both from the US embargo and the totalitarian regime. Castro's (and thus Cuba's) relations with the US have always been frigid, but became icy after the US-backed "Bay of Pigs" attempted coup in 1962. To this day, Cubans who travel to America without permission risk forced repatriation, and Americans who travel to Cuba without official US approval risk hefty fines.
Castro called himself Prime Minister from 1959-76, and then called himself President, though the change was superficial and he was always utterly autocratic. After intestinal surgery in July 2006, he was rarely seen in public. He temporarily ceded power to his brother, Raúl Castro, on 31 July 2006, and formally stepped down as President on 19 February 2008.
Father: Angel Castro y Argiz (sugar plantation owner)
Mother: Lina Ruz Gonzáles (his father's maid)
Brother: Raúl Castro (co-revolutionary and Fidel's successor)
Wife: Mirta Diaz Balart de Nunez (m. 12-Oct-1948; div. 1954, one son)
Son: Fidel Casro Diaz-Balart Jr. (head of Cuba's atomic energy bureau, b. 1-Sep-1949)
Girlfriend: Natalia "Naty" Revuelta (military cap-maker, b. 1925)
Daughter: Alina Fernandez (b. 1956)
High School: Colegio Belén, Havana, Cuba
Law School: University of Havana, Havana, Cuba (1950)
President of Cuba 1959-2008
Order of Lenin
Stalin Peace Prize 1961
Excommunicated by Pope John XXIII 3-Jan-1962
Converted to Atheism
Assassination Attempt multiple
Pardoned
Treason
Risk Factors: Smoking
FILMOGRAPHY AS ACTORLooking for Fidel (14-Apr-2004) Himself
Comandante (18-Jan-2003) Himself
Fidel (2-Aug-2001) Himself
Waiting for Fidel (1974) Himself
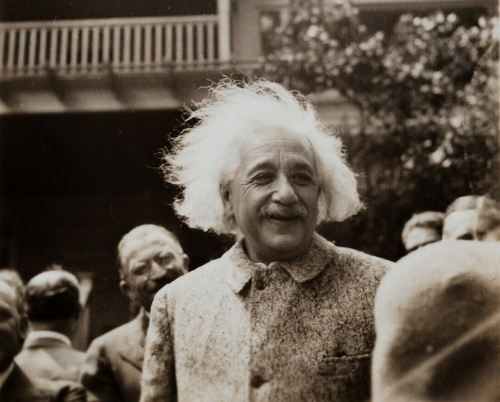
 Albert Einstein was born at Ulm, in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879. Six weeks later the family moved to Munich, where he later on began his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, they moved to Italy and Albert continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland and in 1896 he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. In 1901, the year he gained his diploma, he acquired Swiss citizenship and, as he was unable to find a teaching post, he accepted a position as technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office. In 1905 he obtained his doctor's degree.
Albert Einstein was born at Ulm, in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879. Six weeks later the family moved to Munich, where he later on began his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, they moved to Italy and Albert continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland and in 1896 he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. In 1901, the year he gained his diploma, he acquired Swiss citizenship and, as he was unable to find a teaching post, he accepted a position as technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office. In 1905 he obtained his doctor's degree.




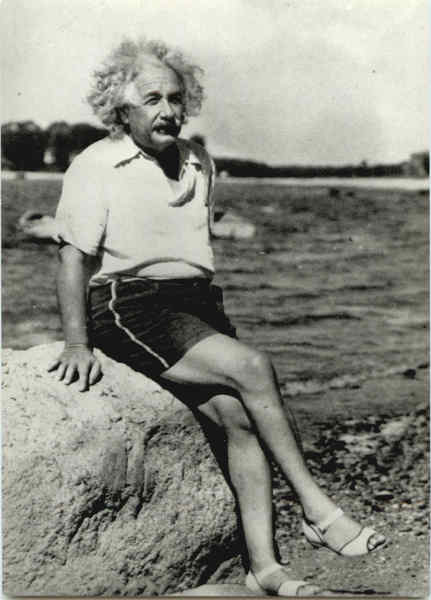




 Mother Teresa was born Agnes Gonxha Bojaxhiu in Skopje
Mother Teresa was born Agnes Gonxha Bojaxhiu in Skopje




![[Diana04s.JPG]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg-A7nR5Qiurr00rx7WN320v3U_MHgwfPy7niI30NGi-tiPCf3baTsnwwEaocRJXyAE_2zhPJL9uiQy7AOhAURg8-EXytE1fNqFrLD0f7wu0-XfQvtEejZIT8ScZFGrGRVJ3h26gCpLnkGV/s1600/Diana04s.JPG)
![[s254.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhbj0udkBGMLUxvQvxT6jKoVjVr25n_xl_Y0p0-D9e3mzBf82ueapdCdsVK0u1J7iu4V_HBOXzUggPJTDB_edW9bxUtuZQTS9cnHw0u4gDC1YrwqI_xp40oll9RNnyJfj0Pg_9OYYfI0tHB/s1600/s254.jpg)
![[mtrp1.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhJBPPm1PtbBjjwWq2lPqb-k1uJaZ3UOhqEouqtN39jVg-kFymBUZweo-bCe0hBFbbCkSYs3JjyoyUS3uI33FKuwZ1b061vON7hcvir7tGyMuDPvzZCclUx1zyODA9_EbED8DWrFEvVcvY0/s1600/mtrp1.jpg)
![[mtrp2.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhkgHScpbdracFYk8X0y_21OD74aDEqB-X-ypiKeaRRV4zsiNrCHPTWoXOBAeAY075t5wSsWuzsgilT0H0kPvt2YXUOAthKzjbD_gqBhblqNTTZJhuueKLhRtxNkM2HnpLCDqR0EhS47O4q/s1600/mtrp2.jpg)
![[thumb.gif]](http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_JkJ4YXh4XnI/R0wfpMTMMCI/AAAAAAAAABc/WDMvFdI0PP0/s1600/thumb.gif)












 looking to her father nehru.
looking to her father nehru.











![[image.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjQgLsP8ykRNT1VPdH0Xuf4WAnhFhbPiOR6KcxVXwSXOXYYa4gHBGWzytu2HfbkaM201SjUIWVMGHkMPpVZoRqG60Yx1KLieMvPA4P_JfxH1a3T3TlV2pA8XTnUyuMSX8yBthrmgygdHr_X/s1600/image.jpg)




